Tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) is often used within the identification of peptides and proteins.
Typical proteomic experiments depend on algorithms reminiscent of SEQUEST and MASCOT to check 1000’s of tandem mass spectra in opposition to the theoretical fragment ion spectra of peptides in a database.
The chances that these spectrum-to-sequence assignments are right could be decided by statistical software program reminiscent of PeptideProphet or by means of estimations based mostly on reverse or decoy databases.
Nevertheless, lots of the software program functions that assign possibilities for MS/MS spectra to sequence matches had been developed utilizing coaching information units from 3D ion-trap mass spectrometers.
Given the number of sorts of mass spectrometers which have develop into commercially accessible over the past 5 years, we sought to generate a knowledge set of reference information protecting a number of instrumentation platforms to facilitate each the refinement of present computational approaches and the event of novel software program instruments.
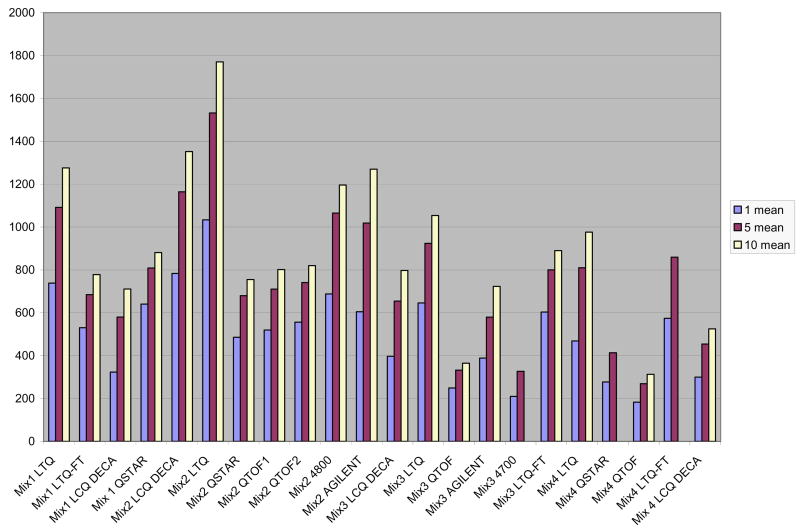
We analyzed the proteolytic peptides in a combination of tryptic digests of 18 proteins, named the “ISB commonplace protein combine”, utilizing eight completely different mass spectrometers.
These embrace linear and 3D ion traps, two quadrupole time-of-flight platforms (qq-TOF), and two MALDI-TOF-TOF platforms.
The ensuing information set, which has been named the Customary Protein Combine Database, consists of over 1.1 million spectra in 150+ replicate runs on the mass spectrometers. The info had been inspected for high quality of separation and searched utilizing SEQUEST.
Comparative analysis of two two-dimensional gel electrophoresis picture evaluation software program functions utilizing synovial fluids from sufferers with joint illness.
The proteomic composition of synovial fluid (SF) could maintain clues to understanding the molecular foundation of arthritis.
Nevertheless, the extremely viscous nature and proteomic complexity of SF current a problem when analyzing outcomes obtained by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2D-GE).
A number of software program functions can be found for analyzing 2D-GE photos. Regardless of inherent strengths and weaknesses, no comparability between these functions has been reported utilizing SF or any human fluid specimens.
We evaluated two widespread software program packages–PDQuest and Progenesis Workstation–for spot detection, matching, and quantitation of 2D-GE photos of SF from 4 sufferers with arthritic illness.
Initially, complete 2D-gel photos had been analyzed for spot detection, which instructed that PDQuest is extra constant than Progenesis; nevertheless, PDQuest appeared to require extra consumer intervention than Progenesis.
Subsequently, two small areas (spots nicely resolved and spots not nicely resolved) had been chosen from every gel picture, which had been analyzed by the software program for spot detection, matching, quantity, and determination.
These analyses counsel that each instruments can quantify well-resolved spots comparatively constantly when put next with guide spot detection (the “gold commonplace”).
The “3D viewer” possibility supplied by each instruments allows right spot identification and matching. The strengths and weaknesses of those pc instruments can present steerage within the alternative of a specific workstation for figuring out biomarkers of arthritis.
